








A singular rapid application platform that scales across your organization to fix issues now!
Be up and running in days – not weeks or months.
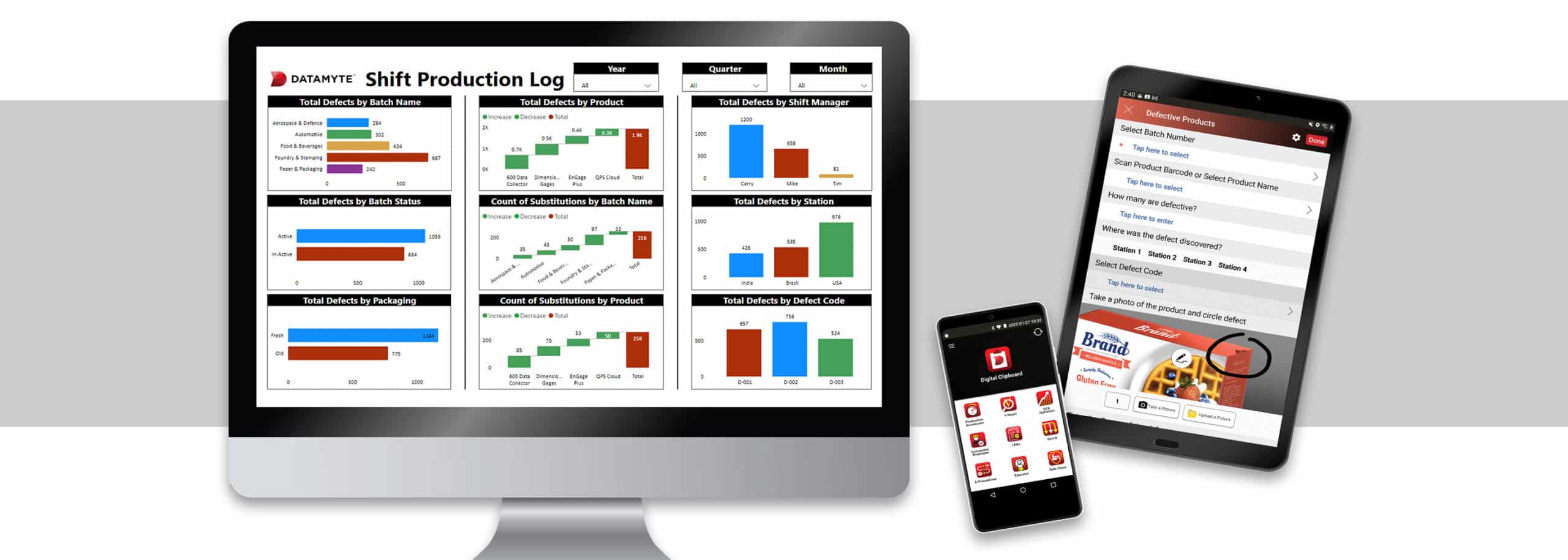
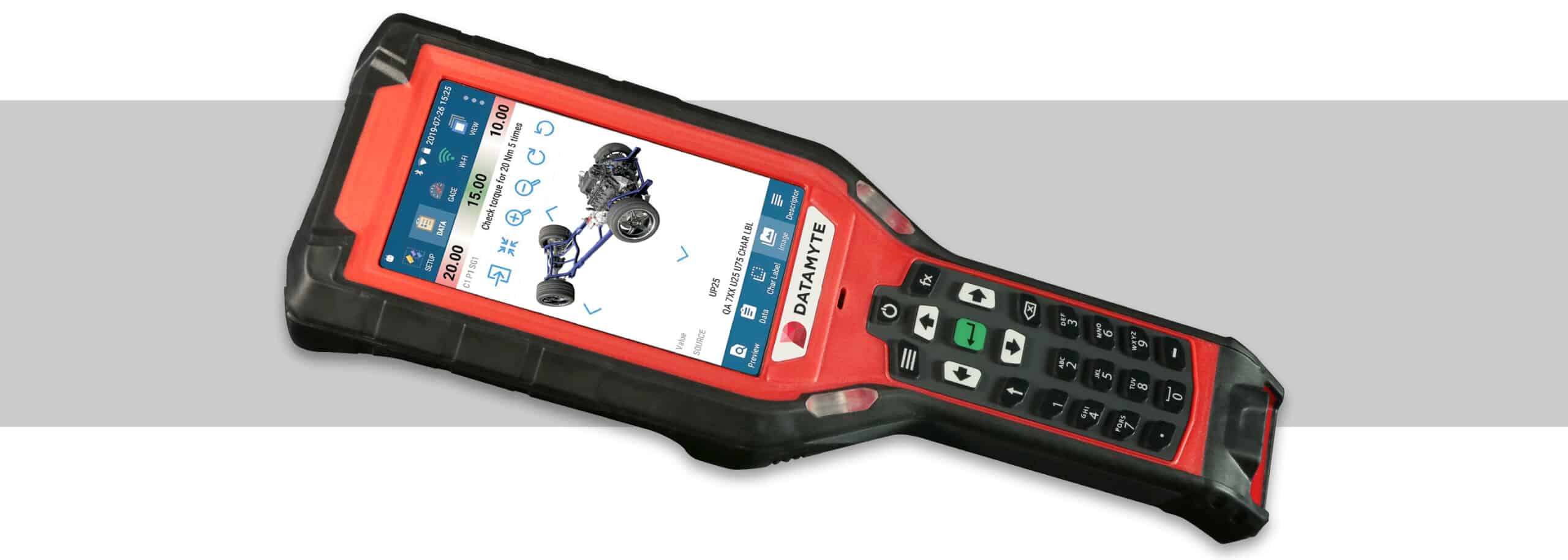
The new generation of durable DataMyte mobile data collectors delivering impeccable data integrity and labor efficiencies. Now with a FREE license of Digital Clipboard on every device.



Start your digital transformation today. Create your account and discover how simple it is to create your own workflows and start catching issues!

